尝试使用LangChain的Agents功能。
Intro
LangChain 官方文档的 Core components 第一项就是 Agents ,我们先来看看官方是如何介绍的 :
Agents combine language models with tools to create systems that can reason about tasks, decide which tools to use, and iteratively work towards solutions.
create_agent provides a production-ready agent implementation.
An LLM Agent runs tools in a loop to achieve a goal. An agent runs until a stop condition is met - i.e., when the model emits a final output or an iteration limit is reached.
这段话告诉我们三个信息:
- Agent 是将语言模型(LLM)与工具(Tools)结合的系统。它的特点是具备推理能力,能自主决定该用什么工具,并通过反复迭代来解决任务。
- 可以使用
create_agent函数实现 - Agent 的运行是一个循环过程:它会不断运行工具,直到满足停止条件为止。
并且给出了简单的工作流程: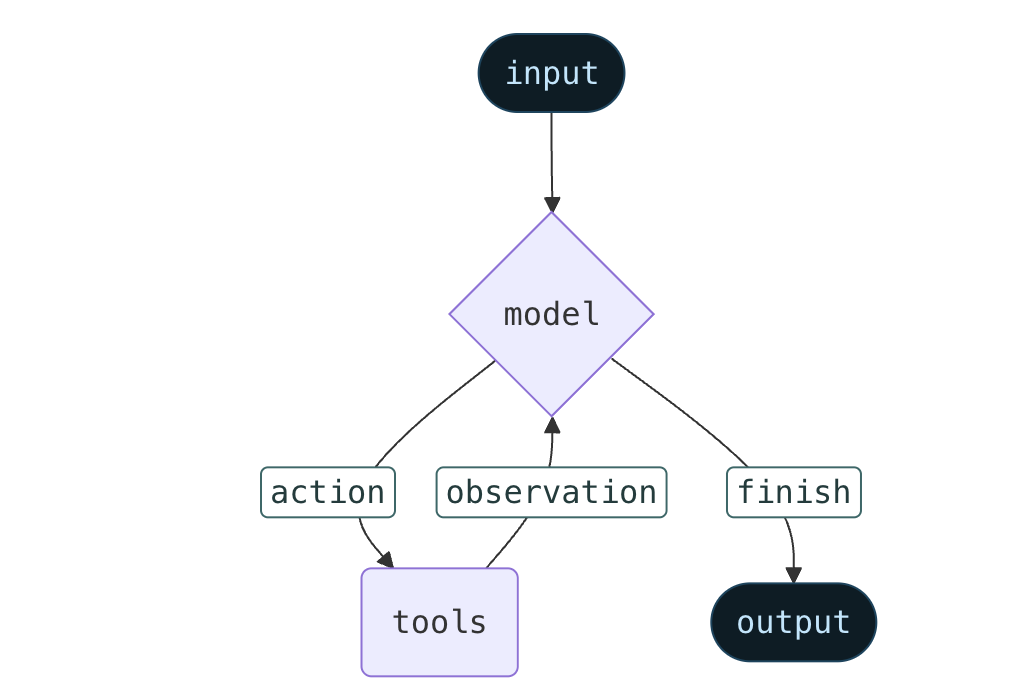
Core components
Model
Model 就是 Agent 的推理引擎,负责思考、决策和生成回复。
对于 LLM 模型的调用分为两种模式:
- Static Model:最常用的方式。在创建 Agent 时就固定好(例如指定用
gpt-4o),整个运行过程中不会变。 - Dynamic Model:一种高级用法,可以在运行时根据上下文动态选择模型。比如在简单的问题上使用便宜的模型。
Tools
Tools 就是 Agent 与外部世界交互的工具。通常是标准的 Python 函数,加上 @tool 装饰器。根据文档的示例,我们可以通过create_agent简单定义一个 Tool :1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15from langchain.tools import tool
from langchain.agents import create_agent
def search(query: str) -> str:
"""Search for information."""
return f"Results for: {query}"
def get_weather(location: str) -> str:
"""Get weather information for a location."""
return f"Weather in {location}: Sunny, 72°F"
agent = create_agent(model, tools=[search, get_weather])
而如果要自定义Tool错误的处理方式,就使用 @wrap_tool_call 装饰器创建中间件:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22from langchain.agents import create_agent
from langchain.agents.middleware import wrap_tool_call
from langchain.messages import ToolMessage
def handle_tool_errors(request, handler):
"""Handle tool execution errors with custom messages."""
try:
return handler(request)
except Exception as e:
# Return a custom error message to the model
return ToolMessage(
content=f"Tool error: Please check your input and try again. ({str(e)})",
tool_call_id=request.tool_call["id"]
)
agent = create_agent(
model="gpt-4o",
tools=[search, get_weather],
middleware=[handle_tool_errors]
)
System Prompt
顾名思义,System Prompt 就是系统层面的提示词,用于设定 Agent 的行为规范和角色。
最简单的定义方式就是在构建agent示例时传入:1
2
3
4
5agent = create_agent(
model,
tools,
system_prompt="You are a helpful assistant. Be concise and accurate."
)
这是传入Str,复杂一些,可以传入LangChain的 SystemMessage.1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23from langchain.agents import create_agent
from langchain.messages import SystemMessage, HumanMessage
literary_agent = create_agent(
model="anthropic:claude-sonnet-4-5",
system_prompt=SystemMessage(
content=[
{
"type": "text",
"text": "You are an AI assistant tasked with analyzing literary works.",
},
{
"type": "text",
"text": "<the entire contents of 'Pride and Prejudice'>",
"cache_control": {"type": "ephemeral"}
}
]
)
)
result = literary_agent.invoke(
{"messages": [HumanMessage("Analyze the major themes in 'Pride and Prejudice'.")]}
)
Invocation
启动 Agent。
Agent 的运行是基于 State (状态) 的更新,通常只需要给它传入一个新的消息(Message),它就会开始根据图(Graph)的逻辑运行,直到得出结果。比如:1
2
3result = agent.invoke(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "What's the weather in San Francisco?"}]}
)
除了以上基础的必要的步骤,LangChain 还为 Agents 提供了一些高级功能。我们简单了解一下:
Structured Output (结构化输出)
可以强制返回 JSON 数据(比如提取出的姓名、日期、订单号),方便程序直接后续处理。
Memory (记忆机制)
- 短期记忆: 通过 State 实现记住这轮对话里你刚才说了什么。
- 长期记忆: 通过数据库实现历史记忆。
Streaming (流式输出)
Agent 可以一边调用工具,一边就在屏幕上即时打印出它的思考过程。
Middleware (中间件)
它可以在 Agent 说话前、说话后,或者工具报错时工作。比如在工具报错时,自动让 Agent 重试,而不是直接让程序崩溃。
这些Agents的功能似乎封装的还不错,那我们来实际尝试一下。
实战
在实战中,我们需要实现一个日常小助手,他有以下两个小功能:
🤖Daily Assistant
WeatherTool: 查询某地天气
Loan Calculator: 计算等额本息
WeatherTool
这是一个天气查询工具。为了查询真实的天气,我们去 OpenWeatherMap 官网申请一个免费的 API Key,然后使用其api查询指定城市的天气。
1 | import os |
在上述代码中,我们先定义了输入参数的结构WeatherInput,其实就是输入一个城市名字符串。随后,继承BaseTool类定义一个RealWeatherTool类,定义内部字段并重写_run方法。
和上一篇笔记一样,我们使用阿里的 qwen 模型,创建一个agent,并把自定义的tool交给他测试一下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21import os
from langchain_community.chat_models import ChatTongyi
from langchain.agents import create_agent
from tools.weathertool import RealWeatherTool
from langchain_core.messages import HumanMessage
os.environ["DASHSCOPE_API_KEY"] = "******"
llm = ChatTongyi(model_name="qwen-max")
weather_tool = RealWeatherTool()
tools = [weather_tool]
agent = create_agent(llm, tools=tools)
query = "帮我查查杭州的天气。"
result = agent.invoke({
"messages": [HumanMessage(content=query)]
})
for message in result["messages"]:
message.pretty_print()
我们打印完整的输出,记录了大模型调用工具的过程:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22=============== Human Message ===============
帮我查查杭州的天气。
=============== Ai Message ================
Tool Calls:
get_real_weather (call_9a7740f492704862b7ae77)
Call ID: call_9a7740f492704862b7ae77
Args:
city: Hangzhou
================ Tool Message ===============
Name: get_real_weather
【Hangzhou 实时天气】
- 状况: 晴
- 温度: 8.95°C
- 湿度: 28%
- 风速: 3.94 m/s
================= Ai Message ===============
杭州现在的天气情况如下:
- 状况: 晴
- 温度: 8.95°C
- 湿度: 28%
- 风速: 3.94 m/s
天气晴朗,外出注意防晒哦!
Loan Calculator
这一部分我们做一个简单的贷款计算器,以实现精准的计算,这是 LLM 不具有的功能。
1 | from typing import Type |
只要在调用时示例化并加入 Tool 列表即可:1
2calculator_tool = LoanCalculatorTool()
tools = [weather_tool, calculator_tool]
Test
我们对上述 Agent 进行一个简单的测试:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48================ Human Message ===============
贷 100 万,30 年,利率 3.25%,每月月供多少?另外,北京今天天气如何?
================ Ai Message ===============
Tool Calls:
calculate_loan_payment (call_2f9e1a62ae0f42cab0eabd)
Call ID: call_2f9e1a62ae0f42cab0eabd
Args:
principal: 1000000
annual_rate_percent: 3.25
years: 30
get_real_weather (call_05f08c54e13747b4b6513d)
Call ID: call_05f08c54e13747b4b6513d
Args:
city: Beijing
================ Tool Message ================
Name: calculate_loan_payment
贷款本金: 1,000,000.00 元
年利率: 3.25%
贷款期限: 30 年 (360 期)
每月月供: 4,352.06 元
总利息: 566,742.75 元
本息合计: 1,566,742.75 元
================ Tool Message ================
Name: get_real_weather
【Beijing 实时天气】
- 状况: 晴
- 温度: -4.06°C
- 湿度: 17%
- 风速: 7.74 m/s
================= Ai Message ================
您的贷款每月月供为 4,352.06 元。下面是详细信息:
- 贷款本金: 1,000,000.00 元
- 年利率: 3.25%
- 贷款期限: 30 年 (360 期)
- 总利息: 566,742.75 元
- 本息合计: 1,566,742.75 元
北京今天的实时天气情况如下:
- 状况: 晴
- 温度: -4.06°C
- 湿度: 17%
- 风速: 7.74 m/s
请注意保暖,外出时可能需要携带外套。